Understanding the Importance of Drying Grains Before Storage

Grain storage is a critical process in agriculture, significantly impacting food security and economic stability. One of the most crucial steps in this process is drying grains before storage. But why is this step so important? In this article, we will explore the reasons behind this necessity, the methods of drying, and how proper drying techniques can enhance the quality and shelf life of grains.
What Happens to Grains When They Are Not Dried?
Before diving into the reasons for drying, it's essential to understand what occurs when grains are stored with high moisture content. Moisture is a primary factor that affects the overall quality and safety of grains. Here are some potential consequences of storing wet grains:
- Development of Mold and Fungi: Excess moisture creates a perfect environment for molds and fungi to thrive. This not only degrades the quality of grains but can also render them unsafe for consumption.
- Insect Infestations: High humidity levels attract pests. Insects such as weevils thrive in damp conditions, potentially leading to significant grain losses.
- Nutritional Degradation: Moisture can lead to the breakdown of essential nutrients, reducing the nutritional quality of the grain.
- Heat Generation: Moist grains can heat up during storage due to microbial activity, leading to further spoilage.
Why is it Necessary to Dry Grains Before Storage?
Now, let's address the question: why is it necessary to dry grains before storage? The answer lies in understanding the benefits associated with proper drying practices:
1. Preventing Spoilage
By drying grains to the appropriate moisture levels, typically below 14% for most cereals, we minimize the risk of spoilage caused by mold, pests, and heat. Dry grains have a significantly lower chance of becoming contaminated and can be safely stored for extended periods.
2. Enhancing Storage Life
Drying grains properly extends their storage life. Grains that are adequately dried can last months or even years without significant degradation, making it easier to manage supply and demand throughout the year.
3. Improving Quality and Market Value
Grains with low moisture content maintain their quality better during storage. This leads to higher market values, as buyers are typically willing to pay more for high-quality, well-preserved grains. Proper drying practices can significantly enhance the financial return for farmers.
4. Nutritional Integrity
When grains are stored at the correct moisture levels, their nutritional content is preserved. Essential vitamins and minerals are less likely to degrade, ensuring that the grains retain their health benefits.
5. Reducing Waste
Moisture management not only preserves the grains but also reduces economic waste. Grain losses due to spoilage and quality degradation can be minimized through proper drying techniques. This contributes to a more sustainable agricultural practice.
Methods for Drying Grains
There are various methods available for drying grains, each with its advantages and considerations. Below are some popular techniques:
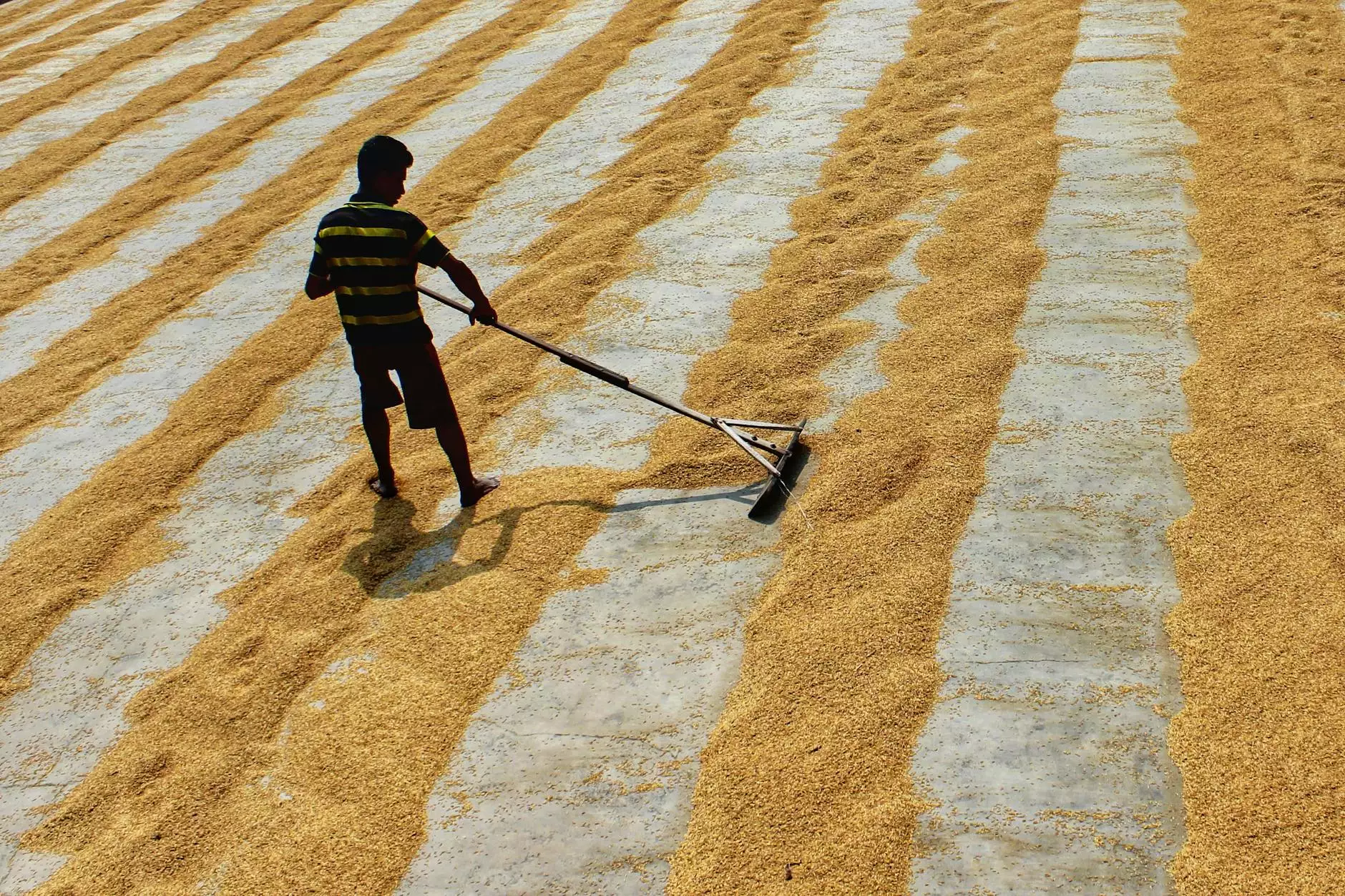
1. Sun Drying
Sun drying is one of the oldest methods of grain drying. This natural process uses sunlight to evaporate moisture, making it a cost-effective choice. However, it requires favorable weather conditions and is time-dependent, making it less reliable in certain climates.
2. Air Drying
Air drying involves using natural or forced airflow to remove moisture from the grains. This method can be employed indoors or outdoors, depending on the resources available. Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent mold growth during air drying.
3. Mechanical Drying
Mechanical dryers are advanced equipment designed to regulate temperature and airflow to achieve efficient grain drying. These devices can be tuned to provide optimal drying conditions, making them one of the most effective methods, especially for large operations.
4. Heat Treatment
Another effective method for drying grains is through the application of heat. This can be done using hot air or other heating mechanisms, effectively reducing moisture levels while preserving grain quality.
Best Practices for Drying Grains
To maximize the benefits of drying grains, it is essential to follow some best practices:
- Monitor Moisture Levels: Regularly check the moisture content of grains during drying to ensure that they reach the desired levels without over-drying.
- Handle Grains Gently: Minimize damage to the grains during handling to avoid excessive breakage, which can lead to quality loss.
- Use Proper Equipment: Invest in reliable drying equipment that suits the scale and type of grains being processed.
- Avoid High Temperatures: Excessive heat can damage grain quality. Maintain moderate drying temperatures to ensure the best outcomes.
- Store in Optimal Conditions: After drying, ensure that grains are stored in a dry, cool, and dark environment to further prevent spoilage.
The Economic Impact of Proper Grain Drying
The implications of effective grain drying extend beyond individual operations to the broader economy. When farmers maximize grain preservation through proper drying, several economic benefits follow:
1. Higher Yields and Profits
Proper moisture management leads to higher yields and significantly increased profits. By minimizing losses during storage, farmers can sell more of their harvested grains at market rates.
2. Enhanced Food Security
When grains are dried correctly, it ensures a more stable food supply. Reduced spoilage and waste mean that more food is available to feed populations, contributing to enhanced food security.
3. Sustainable Farming Practices
Efficient grain drying not only supports economic growth but also promotes sustainable farming practices. By reducing waste and improving the quality of stored grains, farmers can engage in more environmentally-friendly practices.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Grain Drying
Numerous farmers worldwide have experienced the transformative impact of proper grain drying methods. Below are two notable examples:
Case Study 1: A Midwestern Farm Implements Mechanical Drying
A midwestern farmer transitioned from traditional sun drying to a modern mechanical drying system. This shift not only reduced loss from spoilage but also allowed for the processing of larger batches. The farmer reported a 25% increase in profits within the first year, highlighting the economic advantages of grain drying technology.
Case Study 2: Utilizing Solar Drying in Developing Regions
In various developing countries, farmers have begun utilizing solar drying techniques to reduce reliance on electricity and fossil fuels. These sustainable methods have led to improved grain quality and a significant decrease in post-harvest losses, illustrating the effectiveness of combining traditional knowledge with modern innovation.
Conclusion
Drying grains before storage is a fundamental practice that safeguards quality, enhances nutritional value, and prevents spoilage. The methods of drying vary, each with its benefits and considerations, yet the result remains the same—properly dried grains mean healthier, safer food supplies and increased economic stability for farmers. As we advance in agricultural technologies, the importance of optimal grain drying techniques will continue to grow, driving us toward a more sustainable and prosperous agricultural future.
For those engaged in farm equipment repair and management, understanding the nuances of grain drying can provide significant advantages and prop up economies reliant on agriculture. At tsgcinc.com, we are committed to supporting farmers through innovative solutions and expert guidance in grain quality preservation.